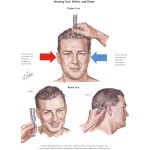
1) Rinne Test -->
After vibrating it, it's put in front of the patient's ears to checked if patient can actually hear the ringing sound. Best if you hear it by yourself first to make sure its a good vibration.
Then put it behind the patient ear just above the tip of the mastoid process. Asked the patient if he/ she is hearing the sounds(not feeling the vibration)and instruct sher to inform once she can't hear. Then, the tuning fork should be shifted in front of the patient ear to check if she still hear anything.Test the other side of the ear as well. Positive Rinne test will mean air conduction which is usually better than bone conduction.
2) Weber Test-->
Again,vibrate the tuning fork using the same way that you're comfortable with before it's put on the center of the patient's forehead/chin(better on the forehead). Ask the patient whether he can hear the sound before you proceed asking whether he can appreciate whether both side of the ears hear equally or 1 side of the ear is hearing better.
If the test Lateralise, or patient hears better on one side of the ear, it means he has either sensorineural hearing loss on the opposite ear or he has conductive deafness of the same side. This should however be confirmed with Absolute Bone Conduction test (ABC)
3) Absolute Bone Conduction test -->
This test is done in the assumption that the examiner actually having both normal conductive and seusorineural hearing ability.
The vibrating tuning fork is placed on the mastoid process again with the tragus of the ear pressed to occlude the external ear meatus (obstruct air conduction).The patient will hear if he has a normal sensorineural conduction of hearing.
Thursday, October 23, 2008
Rinne, Weber and Absolute Bone Conduction Test
Posted by
Wolfie
at
10/23/2008 02:33:00 AM
![]()
Labels: ENT Posting
Subscribe to:
Post Comments (Atom)


2 comments:
Let me know if you think it's good for information or even if there is something for me to correct and add on...Thanks!!
ya...you need to add more on the absolute conduction test..
ABC test concludes normal or conductive deafness if both patient and the examiner hear the sound for same duration of time....its shorter in case of sensorineural deafness..
Post a Comment